S-Glass Fiber,Manufacturing Process of S-Glass Fiber
S-Glass Fiber
Introduction
S-Glass Fiber, short for ‘structural’ glass, is a high-performance material known for its superior strength and chemical resistance. Widely used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment, understanding the manufacturing process sheds light on its remarkable characteristics.
Manufacturing Process of S-Glass Fiber
Glass fibers have become indispensable in various industries, providing strength, durability, and versatility. Among the different types of glass fibers, S-Glass stands out for its exceptional properties, making it a preferred choice in demanding applications. In this article, we will delve into the intricate manufacturing process of S-Glass Fiber, exploring the steps from raw materials to the final product.
What Sets S-Glass Fiber Apart?
Composition and Properties
S-Glass is primarily composed of silica sand, alumina, and magnesium oxide, resulting in a glass matrix with remarkable tensile strength and modulus. Compared to its counterpart, E-Glass, S-Glass exhibits higher mechanical properties.
Comparison with Other Types of Glass Fibers
While E-Glass is the most common type of glass fiber, S-Glass surpasses it in terms of strength and performance. Carbon fiber and aramid fibers are also notable, but S-Glass strikes a balance between cost and performance.
Raw Materials Used in S-Glass Fiber Manufacturing
The manufacturing journey begins with sourcing high-quality raw materials. Silica sand, alumina, and magnesium oxide undergo stringent quality control measures to ensure optimal performance in the final product.
Melting and Forming Process
The raw materials undergo a high-temperature melting process, resulting in a molten glass composition. This molten glass is then formed into strands using specialized equipment, creating the foundational structure for S-Glass Fiber.
Drawing and Coating
The glass strands go through a drawing process, where they are pulled and stretched to achieve the desired diameter. Additionally, a coating is applied to enhance strength and protect against external elements.
Heat Treatment
To relieve internal stresses and enhance mechanical properties, the glass fibers undergo an annealing process. This heat treatment ensures that the S-Glass Fiber achieves optimal performance characteristics.The raw materials are subjected to high-temperature melting, reaching around 1700 degrees Celsius. This intense heat transforms the mixture into a molten state, a crucial step in creating the strong and resilient structure characteristic of S-Glass Fiber.
Sourcing Raw Materials
The journey of S-Glass Fiber begins with carefully selected raw materials, including silica sand, alumina, and other specialized components. These materials undergo a meticulous process to ensure the purity and quality required for the final product.
Applications of S-Glass Fiber
Composition and Structure
At the heart of S-Glass lies silicon dioxide, a key component that distinguishes it from traditional glass fibers. The manufacturing process involves carefully controlling the composition and structure, resulting in a material with superior mechanical properties. This meticulous crafting contributes to its resilience and adaptability.
Strengths and Durability
One of the standout features of S-Glass is its impressive mechanical strength. Compared to conventional E-Glass fiber, S-Glass boasts higher tensile strength and stiffness, making it an ideal candidate for applications demanding structural integrity. Its durability ensures a longer lifespan, reducing maintenance costs in the long run.
Applications in Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace industry, where materials must withstand extreme conditions, S-Glass fiber shines. Aircraft components, from wings to fuselage sections, benefit from its lightweight yet robust nature. Even in spacecraft construction, S-Glass plays a crucial role, providing the necessary strength for space exploration.
Automotive Sector
The automotive sector has embraced S-Glass for high-performance car parts. From body panels to components requiring enhanced impact resistance, the use of S-Glass contributes to improved safety standards. The lightweight characteristic also aids in fuel efficiency, aligning with the industry’s push for sustainability.
Marine and Nautical Applications
In the marine industry, where exposure to saltwater is a constant challenge, S-Glass stands out. Shipbuilding materials incorporating S-Glass fibers exhibit resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for naval applications. This corrosion-resistant property extends the lifespan of maritime structures.
Advantages of Fiber Types
High Bandwidth
Exploring Bandwidth in Fiber
Fiber optics boast unparalleled bandwidth, allowing for high-speed data transfer.
Comparison with Other Types
Compared to traditional copper wiring or coaxial cables, fiber optics outshine competitors in providing consistently high bandwidth, ensuring faster and more efficient data transmission.
Low Latency
Defining Latency in Fiber
Latency, or the delay in data transmission, is significantly reduced in fiber optics.
Comparative Latency Analysis
In a head-to-head comparison, fiber optics exhibit remarkably lower latency when compared to other fiber types, making them ideal for applications where real-time data is critical.
Reliability Comparisons
When reliability is paramount, fiber optics prove to be more dependable than traditional alternatives, ensuring consistent performance even in challenging conditions.
Signal Quality
Understanding Signal Quality
Signal quality is a key factor in data transmission, and fiber optics excel in maintaining signal integrity over longer distances.
Signal Quality in Various Fiber Types
Different fiber types exhibit variations in signal quality, with certain types ensuring superior clarity and consistency in data transmission.
Scalability
Fiber’s Scalability Features
Fiber optics provide scalability, accommodating increased data demands without compromising performance.
Scalability in Comparison
Comparatively, fiber optics offer superior scalability when compared to other fiber types, making them adaptable to evolving technological needs.
Future-Proofing
Adapting to Technological Advancements
Fiber optics prove to be future-proof, seamlessly adapting to technological advancements and ensuring compatibility with emerging technologies.
Real-World Applications
Telecommunications
Fiber optics play a pivotal role in revolutionizing telecommunications, enabling high-speed internet and reliable communication networks.
Internet Services
For internet service providers, the advantages of fiber optics translate into faster and more stable internet connections for end-users.
Industrial Use
Industries leverage fiber optics for robust data transmission in manufacturing processes and automation.
Challenges and Considerations
Installation Costs
While the advantages are evident, it’s essential to consider the initial costs associated with installing fiber optics infrastructure.
Maintenance Factors
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance, and factors like damaged cables may require immediate attention.
Geographical Limitations
In certain remote areas, the installation of fiber optics may pose challenges due to geographical constraints.
Manufacturing Process of S-Glass Fiber
Applications of S-Glass Fiber
Serving Aerospace Excellence
One of the primary applications of S-Glass Fiber is in the aerospace industry. Its lightweight yet robust nature makes it an ideal material for manufacturing components in aircraft and spacecraft, contributing to enhanced fuel efficiency and structural integrity.
Driving the Automotive Sector
The automotive sector has also embraced S-Glass Fiber for its weight reduction benefits and improved crash resistance. Car manufacturers utilize it in the production of body panels, interior components, and even in the development of electric vehicles.
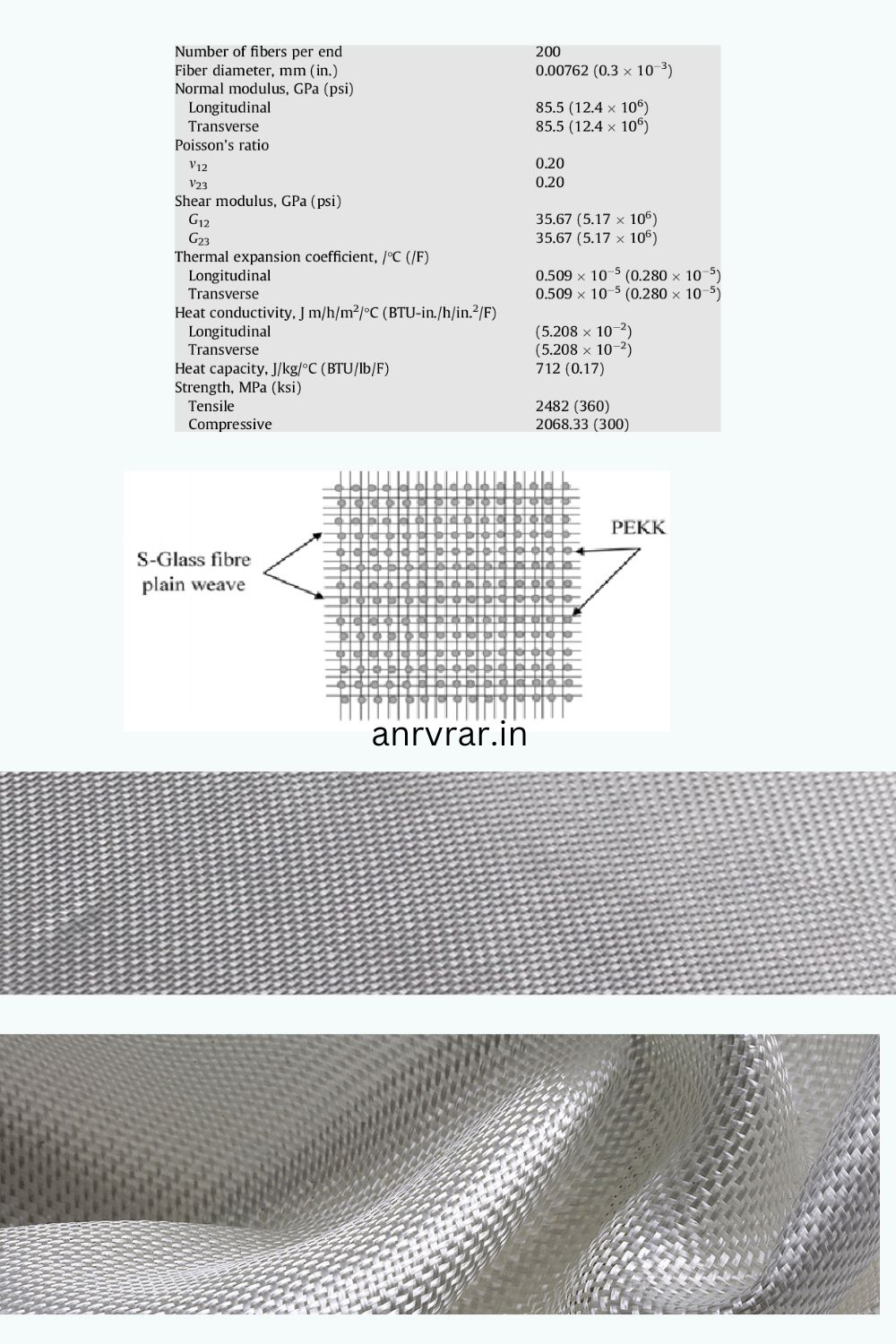
Advantages Over Other Fiber Types
Strength and Durability
S-Glass Fiber boasts an impressive tensile strength, making it stand out among other fiber types. Its durability ensures longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
Chemical Resistance
Unlike some traditional fibers, S-Glass Fiber exhibits remarkable resistance to various chemicals. This property extends its applications to environments where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern.
Thermal Stability
In high-temperature environments, S-Glass Fiber maintains its structural integrity. This thermal stability makes it suitable for applications where exposure to extreme heat is inevitable.
Comparison with E-Glass Fiber
Strength-to-Weight Ratio
S-Glass Fiber surpasses E-Glass Fiber in terms of strength-to-weight ratio, making it a preferred choice in applications where lightweight materials with exceptional strength are crucial.
Cost Considerations
While S-Glass Fiber offers superior performance, it comes at a higher cost compared to E-Glass Fiber. Industries must weigh the benefits against the budgetary considerations when choosing between the two.
Recent Developments
Ongoing research and technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of S-Glass Fiber capabilities. Innovations in manufacturing processes and coating materials aim to further enhance its properties and broaden its range of applications.
Future Prospects
As industries recognize the benefits of S-Glass Fiber, the material is expected to play a pivotal role in future technological developments. From space exploration to everyday consumer products, the versatility of S-Glass Fiber opens doors to innovative possibilities.
Environmental Impact
Recycling Possibilities
Concerns about environmental impact have led to investigations into recycling S-Glass Fiber. While challenges exist, ongoing efforts are focused on developing sustainable practices for the production and disposal of S-Glass Fiber materials.
Green Alternatives
Researchers are exploring eco-friendly alternatives and production methods to mitigate the environmental impact of S-Glass Fiber. The industry is actively seeking ways to balance performance with sustainability.
Challenges in S-Glass Fiber
Cost Challenges
The high production cost of S-Glass Fiber remains a challenge for widespread adoption. Industries must evaluate the long-term benefits against initial investment costs to justify its use in various applications.
Limited Application Expertise
Some industries may be unfamiliar with the intricacies of working with S-Glass Fiber. Overcoming this knowledge gap is crucial to unlocking the full potential of this advanced material.
Positive Impact
Industries that have embraced S-Glass Fiber report positive impacts on performance, safety, and overall efficiency. The material’s unique properties contribute to the success of various projects, creating a ripple effect in different sectors.
S-Glass Fiber in the Construction Industry
Reinforcement in Concrete
In the construction industry, S-Glass Fiber plays a crucial role in reinforcing concrete structures. Its high tensile strength and resistance to environmental factors make it an ideal candidate for enhancing the durability of buildings and infrastructure.
Architectural Applications
Architects and builders appreciate the flexibility that S-Glass Fiber brings to architectural design. From creating intricate facades to ensuring the longevity of structures, the material opens avenues for innovative construction practices.
The Future of S-Glass Fiber
Research and Development
Ongoing research endeavors are focused on pushing the boundaries of S-Glass Fiber. Collaborations between academic institutions and industries aim to unlock new possibilities and refine existing applications.
Emerging Trends
As technology evolves, S-Glass Fiber is anticipated to become a staple in various sectors. Emerging trends include its integration into wearable technology, advancements in medical devices, and breakthroughs in energy storage applications.
Industry Professionals’ Perspectives
Experts in the field emphasize the transformative impact of S-Glass Fiber. Their insights shed light on the material’s potential to revolutionize industries, driving advancements in technology and manufacturing.
Potential Growth Areas
Identifying potential growth areas is crucial for industries looking to capitalize on S-Glass Fiber. From renewable energy solutions to advancements in transportation, the material’s versatility opens doors to diverse opportunities.
Guidelines for Working with S-Glass Fiber
Safety Measures
Working with S-Glass Fiber requires adherence to strict safety measures. Protective gear, proper ventilation, and training are essential to ensure the well-being of workers involved in the manufacturing and application processes.
Best Practices
Following best practices in handling, cutting, and molding S-Glass Fiber is crucial for maximizing its performance. Industries should invest in proper training to optimize the material’s benefits and mitigate risks.
Recap of Key Points
In conclusion, S-Glass Fiber stands as a formidable player in the world of composite materials. From its inception in the aerospace industry to its widespread applications in construction, automotive, and sports, S-Glass Fiber has proven its worth in diverse settings.
Importance of S-Glass Fiber
Its exceptional strength, durability, and chemical resistance make it a go-to choice for industries seeking high-performance materials. As technology advances, S-Glass Fiber is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of various sectors.https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/physics-and-astronomy/s-glass
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes S-Glass Fiber unique?
S-Glass Fiber is unique due to its exceptional strength, durability, and chemical resistance, making it a versatile material for various applications.
How does S-Glass Fiber contribute to sustainability?
While challenges exist, ongoing research aims to develop sustainable practices for the production and disposal of S-Glass Fiber, addressing environmental concerns.
Are there any limitations to S-Glass Fiber?
Challenges include its higher production cost and the need for industries to overcome limited expertise in working with this advanced material.
Can it replace traditional construction materials?
S-Glass Fiber is increasingly being used in construction, reinforcing concrete structures and offering flexibility in architectural design, showcasing its potential to replace or enhance traditional materials.
Where can one find S-Glass Fiber products?
S-Glass Fiber products are used in aerospace components, automotive parts, sports equipment, and construction materials. They can be sourced from specialized suppliers and manufacturers.
Is S-GLASS FIBRE suitable for high-temperature applications?
Yes, S-GLASS FIBRE excels in high-temperature environments, making it ideal for aerospace and other industries.
How does S-GLASS compare to traditional fiberglass?
S-GLASS offers superior strength and temperature resistance compared to traditional fiberglass.
Is S-GLASS FIBRE environmentally friendly?
Absolutely, S-GLASS FIBRE is recyclable and contributes to sustainable practices.
What challenges are associated with using S-GLASS FIBRE?
Challenges include cost considerations, availability, and addressing specific application requirements.
Can S-GLASS FIBRE be used in consumer products?
Yes, S-GLASS FIBRE finds applications in various consumer products due to its strength and durability.
