HOW MANY MAKING METHOD OF FRP
THERE ARE SEVEN MAKING METHOD OF FIBERGLASS REINFORCED POLYMER (FRP)
1.Hand Lay-up
2.Spray up method
3.Filament winding
4.Match die molding
5.Pultrusion
6.Resin transfer molding
7.Reaction injection molding
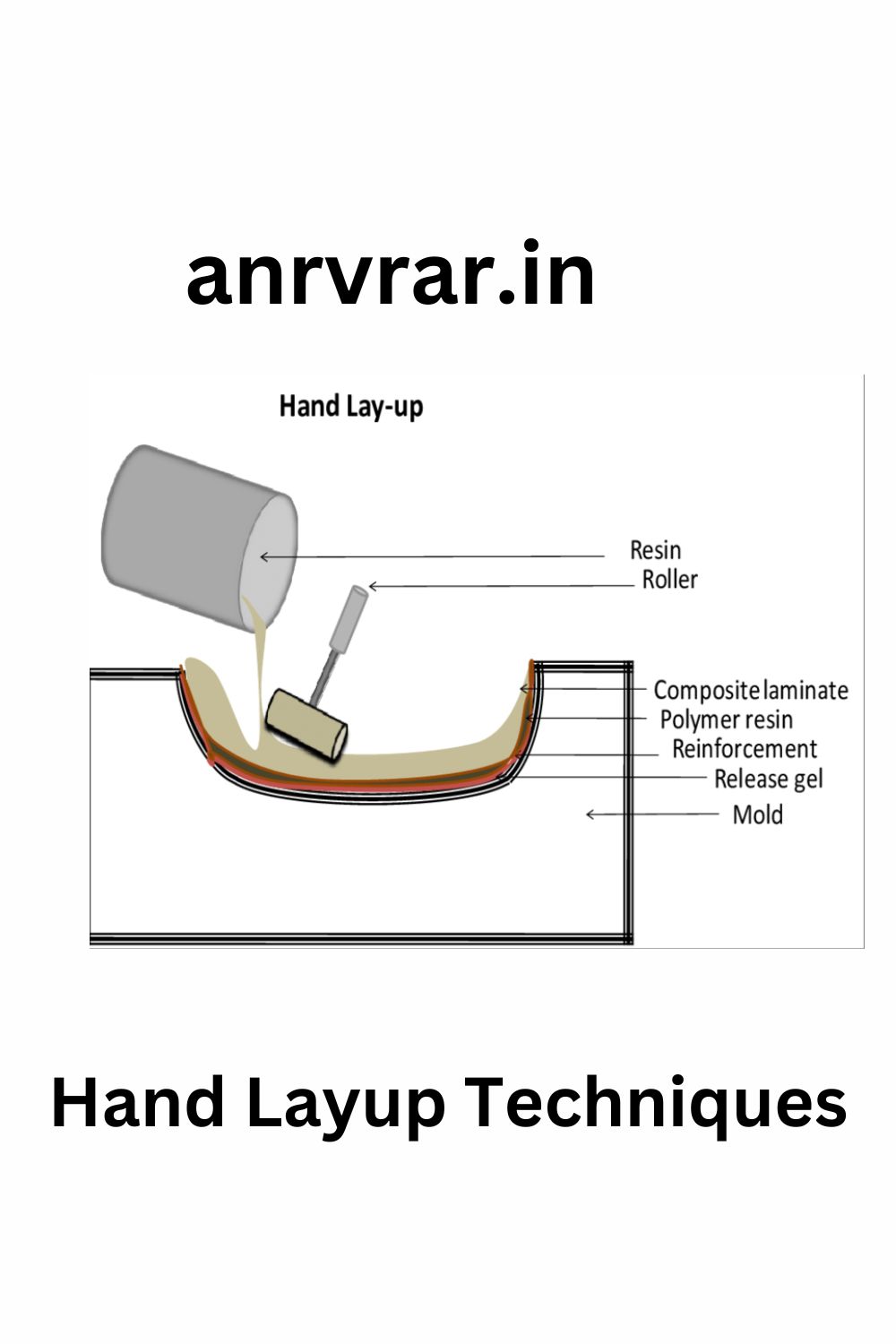
1.Hand Lay-Up Process;
This method can be used for both the corrosion barrier and the structural portion. A mold must be used for hand lay-up parts unless the composite is to be joined directly to another structure. The mold can be as simple as a flat sheet or have infinite curves and edges. For some shapes, molds must be joined in sections so they can be taken apart for part removal after curing.
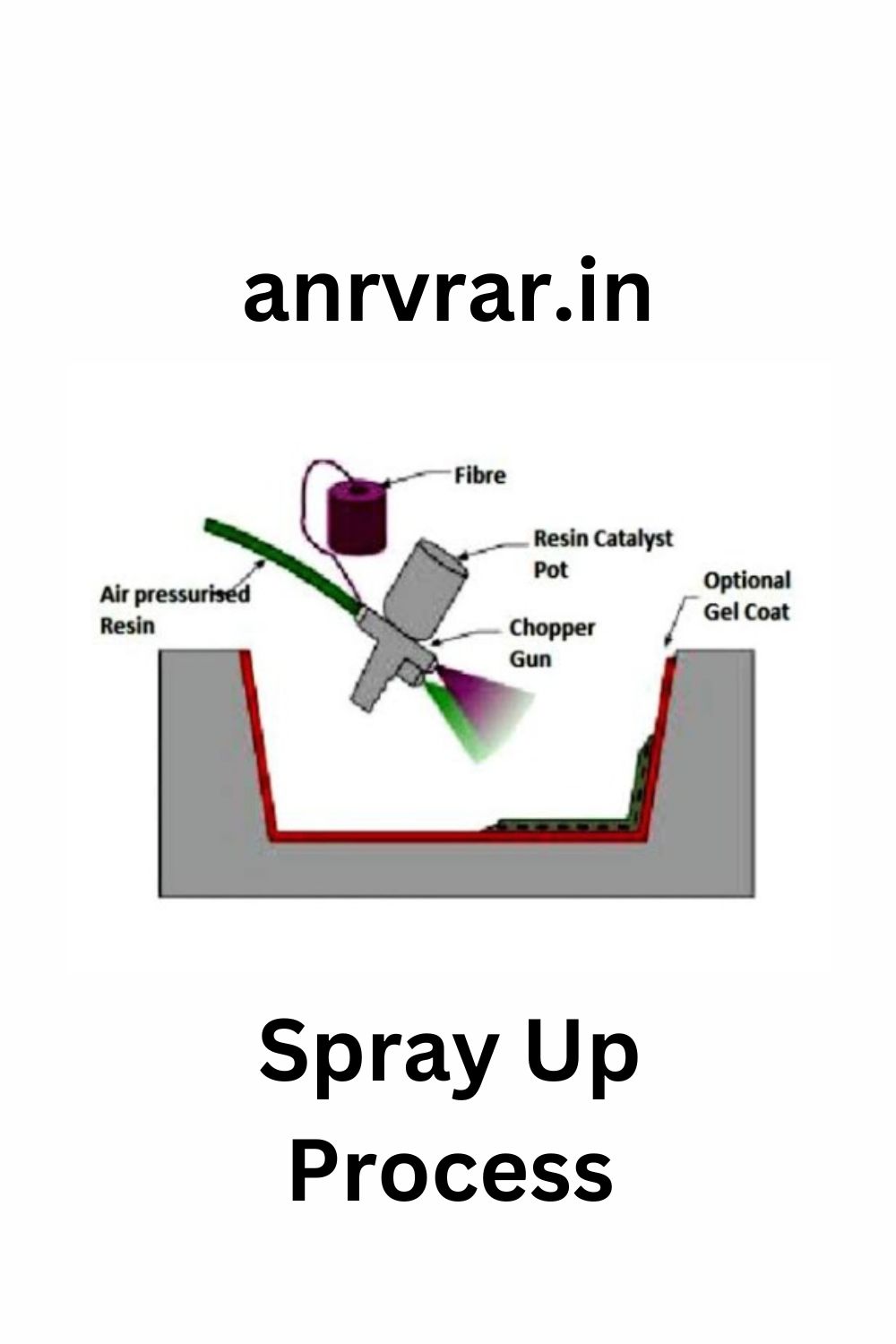
2.Spray Up Method
Fibre is chopped in a hand-held gun and fed into a spray of catalysed resin directed at the mould. The deposited materials are left to cure under standard atmospheric conditions.
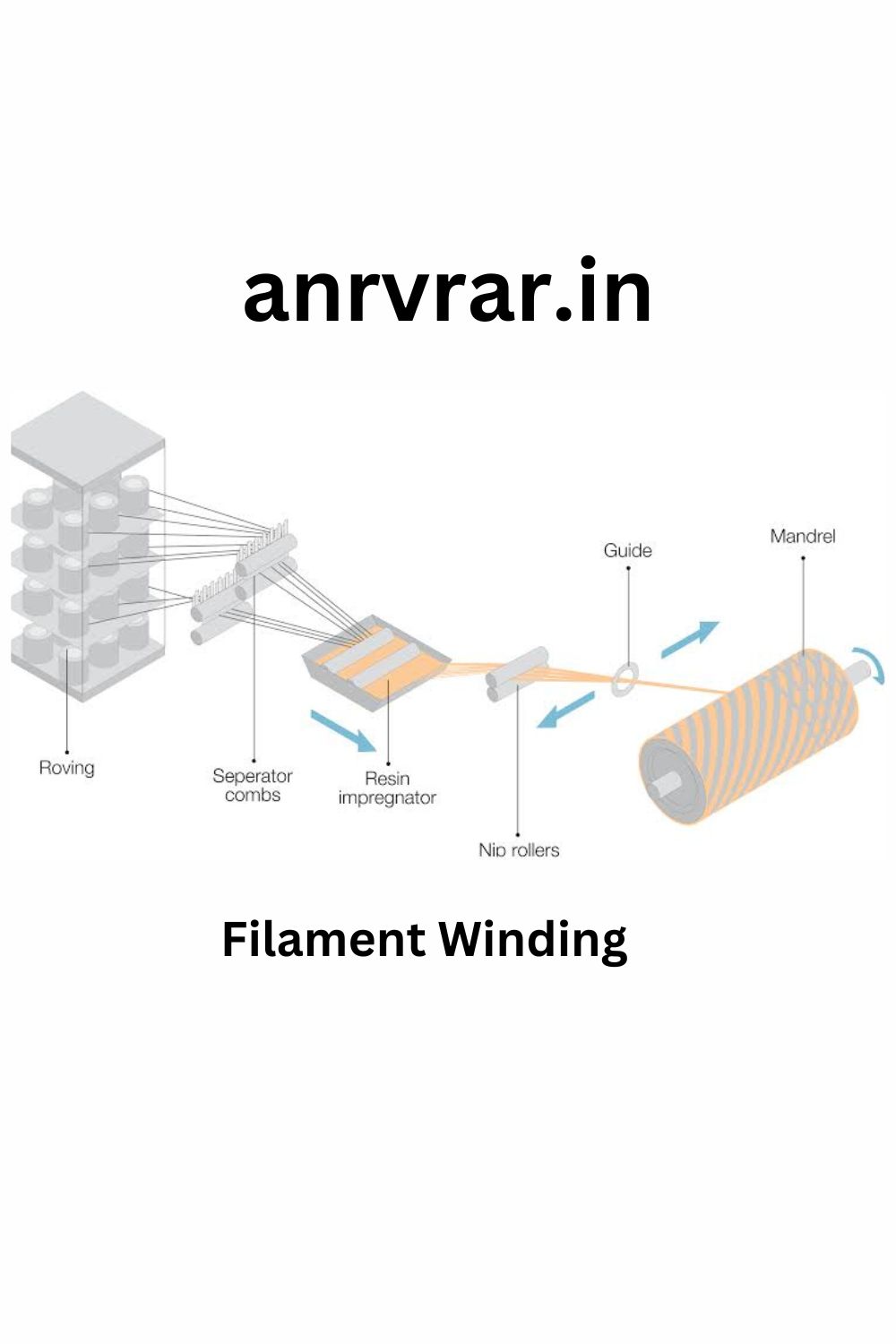
3.Filament winding
This process is primarily used for hollow, generally circular or oval sectioned components, such as pipes and tanks. Fibre tows are passed through a resin bath before being wound onto a mandrel in a variety of orientations, controlled by the fibre feeding mechanism, and rate of rotation of the mandrel.
4.Match die molding
The composite material is pressed between heated matched dies -Pressure required depends on the flow characteristics of the feed materials – The feed materials flows into the contours of the mould and cures at high temp.
5.Pultrusion
Fibres are pulled from a creel through a resin bath and then on through a heated die. The die completes the impregnation of the fibre, controls the resin content and cures the material into its final shape as it passes through the die. This cured profile is then automatically cut to length. Fabrics may also be introduced into the die to provide fibre direction other than at 0°. Pultrusion is a continuous process, producing a profile of constant cross-section, a variant known as ‘pulforming’ allows for some variation to be introduced into the cross- section.
6.Resin transfer molding
In this technique, as the name indicates, resin is transferred over the already placed reinforcement . Reinforcement in terms of either woven mat or strand mat form is placed on the surface of lower half mold.
A release gel is applied on the mold surface for easy removal of the composite. The mold is properly closed and clamped. The clamping can be done either perimeter clamping or press clamping mechanism . The resin is pumped into the mold through ports and air is displaced through other vents. After curing, the mold is opened and composite product is taken out
7.Reaction injection molding
Reaction injection molding (RIM) is similar to injection molding except thermosetting polymers ar e used, which requires a curing reaction to occur within the mold.
First, the two parts of the polymer are mixed together. The mixture is then injected into the mould under high pressure using an impinging mixer. The mixture is allowed to sit in the mole long enough for it to expand and cure. If reinforcing agents are added to the mixture then the process is known as reinforced reaction injection moulding . Common reinforcing agents include glass fibers and mica. This process is usually used to produce rigid foam automotive panels
Materials Options: Resins: Primarily polyester. Fibres: Glass roving only.https://anrvrar.in/wp-admin/post.php?post=41&action=edit
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fibre-reinforced_plastic#Process_definition

Thank you for sharing this article with me. It helped me a lot and I love it.
Can you write more about it? Your articles are always helpful to me. Thank you!
YES
Thank you for providing me with these article examples. May I ask you a question?
Can you write more about it? Your articles are always helpful to me. Thank you!
why not
Outstanding post however I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Bless you!
I was just looking for this information for some time. After six hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your website. I wonder what is the lack of Google strategy that do not rank this type of informative websites in top of the list. Usually the top sites are full of garbage.
It抯 really a great and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
Thanks for your post. One other thing is that often individual states in the United states of america have their unique laws that affect home owners, which makes it extremely tough for the the nation’s lawmakers to come up with a fresh set of recommendations concerning foreclosures on home owners. The problem is that a state has own laws and regulations which may have interaction in an adverse manner in relation to foreclosure insurance policies.