Continuous Lamination Quality Control: Beyond Excellence.
Continuous Lamination
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced industrial landscape, innovation is the key to staying ahead. One such groundbreaking technology making waves is Continuous Lamination. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this transformative process that is reshaping industries.
Continuous Lamination is not just a manufacturing process; it’s a revolution in how we enhance materials. This technique involves the continuous application of layers, creating a seamless and durable composite. The result? Superior quality products that outperform traditional counterparts.
The core advantage of Continuous Lamination lies in the strength and durability it imparts to materials. Whether it’s in aerospace, automotive, or construction, products fortified through this method exhibit unmatched resilience. This translates to longer lifespans and reduced maintenance costs.
Steric’s commitment to excellence is evident in the precision engineering redefined by Continuous Lamination. Each layer is meticulously applied, ensuring uniformity and eliminating weak points. This not only enhances structural integrity but also allows for the creation of intricate designs with unparalleled accuracy.
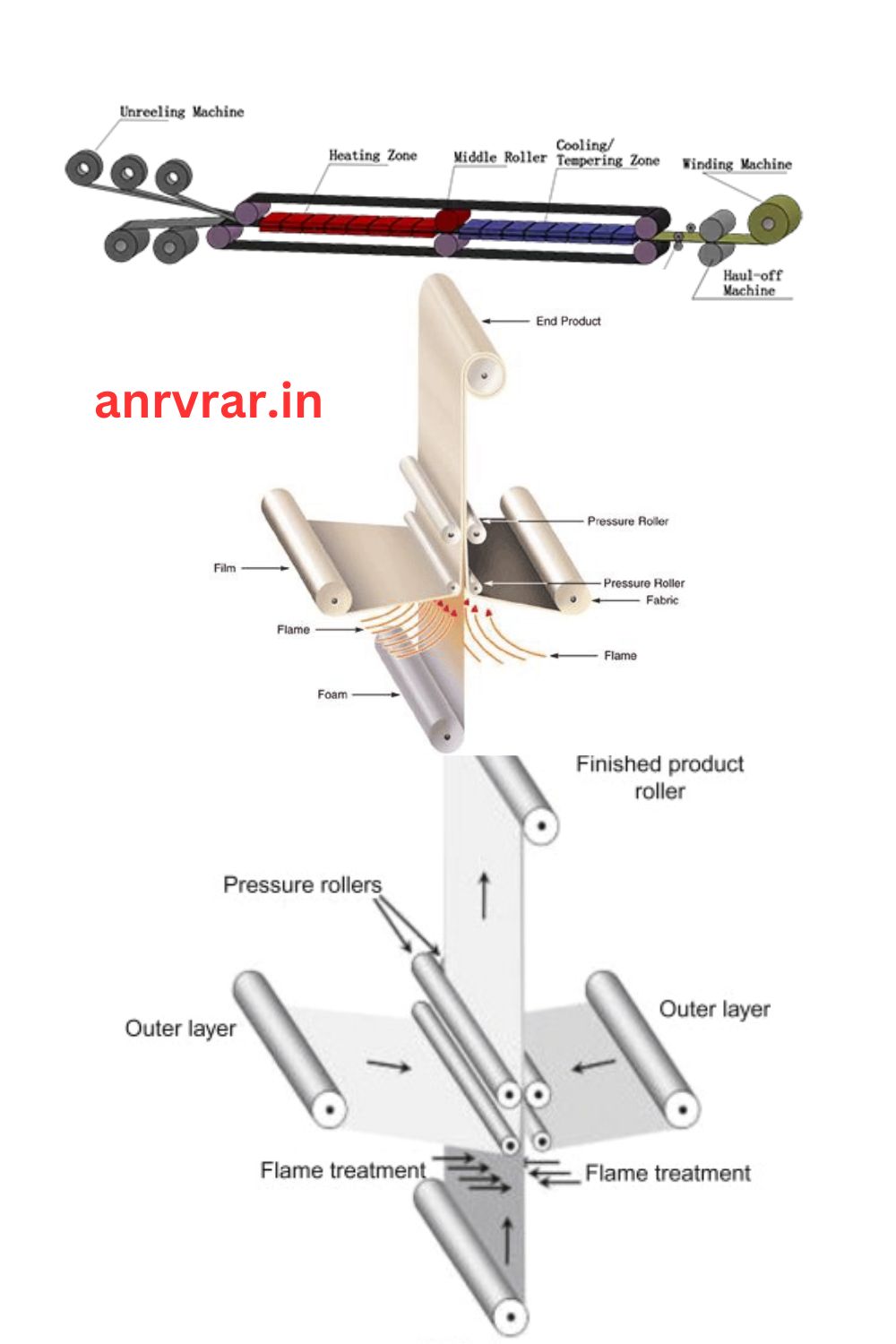
Key Components of Continuous Lamination
The Foundation
Continuous lamination, a cutting-edge manufacturing method, involves the seamless creation of composite materials. This process stands out for its ability to produce consistent and high-quality laminates with minimal waste. As industries evolve, understanding the key components becomes paramount.
Cutting-Edge Machinery
In the world of continuous lamination, sophisticated machinery takes center stage. High-tech laminators, equipped with precision controls, ensure uniformity and accuracy in the lamination process. These machines, a fusion of innovation and engineering, contribute significantly to the efficiency of the entire operation.
Resins and Adhesives
The choice of resins and adhesives plays a pivotal role in the success of continuous lamination. These substances not only bond materials seamlessly but also determine the durability and versatility of the final product. Industries can select from a spectrum of options, tailoring the lamination process to meet specific requirements.
Automated Controls
Automation is the heartbeat of continuous lamination. From material feeding to curing, automated controls ensure precision at every stage. This not only enhances the speed of production but also minimizes errors, resulting in a flawless end product. The synergy of human expertise and automated systems elevates the entire lamination process.
Increased Productivity
The continuous nature of the lamination process leads to a significant boost in productivity. As compared to traditional methods, where interruptions are commonplace, continuous lamination ensures a seamless flow of production, reducing downtime and enhancing overall efficiency.
Waste Reduction
One of the standout advantages of continuous lamination is its minimal waste generation. The precision-driven process optimizes material usage, contributing to a sustainable and eco-friendly manufacturing approach. In a world increasingly focused on environmental responsibility, continuous lamination emerges as a beacon of sustainability.
Customization Options
Continuous lamination empowers industries with a vast array of customization options. From varying material combinations to adjusting lamination thickness, this technique allows for the creation of tailor-made solutions. This flexibility is invaluable across diverse sectors, from aerospace to automotive industries.
Material Breakthroughs
Continuous lamination is not immune to the swift evolution of materials. Ongoing R&D efforts focus on discovering new materials that enhance the strength, flexibility, and overall performance of laminates. These material breakthroughs promise to open new possibilities across industries, from construction to electronics.
Energy Efficiency
The future of manufacturing is inherently linked to sustainability. Continuous lamination, in its journey forward, places a growing emphasis on energy efficiency. Innovations in curing processes, energy-conscious machinery, and eco-friendly resins contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing ecosystem.
Quality Control Measures
Maintaining impeccable quality is an ongoing challenge in the realm of continuous lamination. Rigorous quality control measures, including advanced inspection technologies and real-time monitoring, are being developed to ensure that each product meets the highest standards. This commitment to quality is non-negotiable as industries increasingly demand flawless laminates.
Cost-Effective Solutions
In a competitive market, balancing excellence with cost-effectiveness is paramount. Ongoing efforts focus on streamlining processes without compromising quality. Manufacturers are investing in innovative solutions to make continuous lamination not just efficient but also economically viable for a broad spectrum of applications.
Smart Manufacturing: A Technological Revolution
The marriage of continuous lamination with smart manufacturing ushers in a new era. Sensors embedded in machinery provide real-time data, allowing for predictive maintenance and performance optimization. This interconnected ecosystem ensures that continuous lamination remains not just a manufacturing process but a technologically advanced one.
Applications Across Industries
Aerospace Industry:
Composite Aircraft Components:Continuous lamination is widely used in the aerospace industry to manufacture lightweight and durable composite components for aircraft, such as wings, fuselages, and interior panels.
Automotive Industry:
Vehicle Body Panels:Continuous lamination is employed to produce composite materials used in automotive body panels, reducing weight and improving fuel efficiency without compromising on strength.
Construction and Infrastructure:
Fiber-Reinforced Concrete:Continuous lamination is utilized to create fiber-reinforced composites for construction applications, enhancing the strength and durability of structures such as bridges, buildings, and tunnels.
Renewable Energy:
Wind Turbine Blades:Continuous lamination is crucial in the manufacturing of large and lightweight composite materials used in wind turbine blades. This helps in maximizing energy capture and minimizing structural weight.
Marine Industry:
Boat Hulls and Components:Continuous lamination is applied to produce composite materials for boat hulls and various components, providing high strength, corrosion resistance, and reduced weight.
Sports and Recreation:
Sporting Goods:Continuous lamination is used in the production of sporting goods like carbon fiber-reinforced tennis rackets, golf clubs, and bicycle frames, enhancing performance through lightweight and durable materials.
Medical Devices:
Orthopedic Implants:Continuous lamination is employed in the manufacturing of composite materials for orthopedic implants, providing strength and flexibility required for medical devices like bone plates and joint implants.
Electronics and Technology:
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs):Continuous lamination is used in the production of PCBs, contributing to the fabrication of high-density, lightweight electronic components.
Consumer Goods:
Consumer Electronics:Continuous lamination is applied in the production of lightweight and durable casings for consumer electronic devices, contributing to the sleek and modern design of products like laptops and smartphones.
Packaging Industry:
Flexible Packaging:Continuous lamination is utilized in the production of flexible packaging materials, providing barrier properties, strength, and printability for a wide range of products.
Continuous lamination techniques continue to evolve, enabling the creation of advanced materials with tailored properties to meet the specific needs of diverse industries. The benefits of reduced weight, increased strength, and design flexibility make continuous lamination a valuable manufacturing process across a broad spectrum of applications.
Advantages of Continuous Lamination
Quality Reinforcement Through Precision
Precision is paramount in manufacturing, and continuous lamination is a precision maestro. This technique ensures a consistent quality output by eliminating variations often encountered in batch processes. The meticulous control over each step guarantees that the final product meets the highest standards, earning your business a reputation for excellence.
Cost-Effective Production with Waste Reduction
In the realm of cost-effectiveness, continuous lamination takes center stage. By minimizing material waste and optimizing resources, this technology slashes production costs significantly. The eco-friendly approach not only benefits your bottom line but also aligns your business with sustainable practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
Swift Adaptability to Varied Materials
Versatility is a hallmark of continuous lamination. Whether you’re working with composites, fabrics, or films, this technology seamlessly adapts to different materials. This flexibility opens doors to a myriad of applications across industries, offering a wide spectrum of possibilities for manufacturers looking to diversify their product range.
Strength and Durability
When it comes to the end product, strength and durability are non-negotiable. Continuous lamination excels in enhancing these crucial attributes. The uniform distribution of materials during the lamination process results in products with superior strength and durability, meeting or exceeding industry standards.
Future-Proofing Your Production Line
Investing in continuous lamination isn’t just about the present; it’s a strategic move for the future. As technology evolves, so does continuous lamination, ensuring that your production line remains at the forefront of innovation. Future-proof your business by embracing a technology that adapts and evolves with the dynamic landscape of manufacturing.
Seamless Integration for Operational Harmony
The beauty of continuous lamination lies not only in its operational efficiency but also in its seamless integration into existing workflows. Manufacturers can incorporate this technology without the need for a complete overhaul, minimizing disruption and ensuring a smooth transition. The adaptability of continuous lamination makes it a strategic choice for companies aiming to evolve without compromising on ongoing productivity.
Reducing Lead Times for Swift Market Response
In the ever-evolving market landscape, agility is a competitive advantage. Continuous lamination significantly reduces lead times in the production cycle. This swift turnaround enables businesses to respond promptly to market demands, stay ahead of trends, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. In a world where timing is everything, continuous lamination becomes a catalyst for staying one step ahead.
Challenges and Solutions of Continuous Lamination
Challenges
Material Compatibility Hurdles
Continuous lamination often grapples with the challenge of ensuring compatibility between diverse materials. This hurdle demands a meticulous selection process to guarantee optimal performance and durability.
Precision in Process Control
Achieving precision in the control of the lamination process poses another formidable challenge. Maintaining the delicate balance between speed, pressure, and temperature is imperative, requiring advanced technologies and vigilant oversight.
Environmental Variables
External factors, such as fluctuations in temperature and humidity, can significantly impact the quality of continuous lamination. Addressing these environmental variables becomes paramount to maintain consistency in production.
Solutions
Advanced Material Analysis and Selection
To combat material compatibility issues, industries are investing in advanced material analysis techniques. Employing cutting-edge technologies allows for a comprehensive understanding of materials, ensuring seamless integration within the lamination process.
Automated Process Control Systems
The era of manual control is gradually fading with the adoption of automated systems. Integrated sensors and real-time monitoring enable precise control, minimizing errors and enhancing the overall efficiency of continuous lamination.
Climate-Controlled Facilities
Acknowledging the influence of environmental factors, many industries are opting for climate-controlled facilities. This strategic move mitigates the impact of temperature and humidity variations, fostering a stable production environment.
Innovations in Continuous Lamination
The Power of Seamless Integration
Continuous lamination’s prowess lies in its seamless integration into existing manufacturing workflows. Manufacturers across industries are embracing this technology for its ability to enhance product quality while optimizing resource utilization. The synergy between traditional methods and modern continuous lamination is paving the way for unprecedented advancements.
High-Tech Lamination Machinery
Enter the era of precision with state-of-the-art lamination machinery. These technological marvels are designed to meet the demands of intricate designs and complex material compositions. From aerospace components to automotive interiors, the precision offered by continuous lamination is reshaping industries that demand nothing short of perfection.
Eco-Friendly Lamination Solutions
In response to the global call for sustainable practices, continuous lamination has evolved to offer eco-friendly solutions. The integration of recyclable materials and energy-efficient processes is positioning continuous lamination as a frontrunner in environmentally conscious manufacturing. Companies adopting these innovations not only elevate their production standards but also contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.
Speed, Efficiency, and Cost-Effectiveness
Continuous lamination is not just a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic investment. The speed and efficiency of continuous lamination processes translate into reduced production timelines, minimizing costs without compromising on quality. This trifecta of advantages is reshaping the manufacturing landscape, making it more competitive and adaptive.
Embracing Change: The Role of Continuous Learning
To fully harness the potential of continuous lamination innovations, a culture of continuous learning is imperative. Training the workforce to adapt to the evolving technological landscape ensures that industries stay at the forefront of innovation. Investing in the knowledge and skills required to operate and optimize continuous lamination systems is an investment in long-term success.
In conclusion, continuous lamination innovations are rewriting the rulebook for manufacturing excellence. From precision engineering to sustainable practices, the impact of these advancements is far-reaching. Embracing the transformative power of continuous lamination is not just a choice; it’s a strategic imperative for industries aspiring to lead in the era of technological evolution.
Exploring Potential Applications
The versatility of continuous lamination extends beyond conventional manufacturing. Industries are increasingly exploring diverse applications, from enhancing the durability of consumer electronics to improving the structural integrity of renewable energy components. The adaptability of continuous lamination positions it as a catalyst for innovation across various sectors.
Overcoming Challenges: The R&D Frontier
In the pursuit of excellence, continuous lamination faces its share of challenges. Research and development (R&D) efforts are underway to overcome hurdles and unlock new possibilities. Innovators are tirelessly working on refining materials, perfecting processes, and pushing the boundaries of what continuous lamination can achieve. These endeavors promise a future where limitations are merely stepping stones to greater advancements.
Collaborative Ecosystems: Industry Partnerships
A thriving ecosystem is emerging around continuous lamination, fueled by collaborative partnerships between manufacturers, technology providers, and research institutions. This collaborative spirit amplifies the impact of continuous lamination innovations, fostering an environment where shared knowledge and expertise drive progress. The synergies created through these partnerships propel the industry forward, ensuring a collective march towards excellence.
Investing in Tomorrow: Continuous Lamination as a Strategic Asset
For forward-thinking businesses, viewing continuous lamination as a strategic asset is paramount. Those who invest in the latest advancements are not just responding to current demands; they are future-proofing their operations. As industries evolve, the ability to adapt and integrate the latest continuous lamination technologies becomes a competitive advantage that sets leaders apart from followers.
Regulatory Landscape: Navigating Compliance in Continuous Lamination
As continuous lamination becomes more ingrained in manufacturing processes, understanding and navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial. Compliance with industry standards and regulations ensures the seamless adoption of these innovations. Manufacturers must stay abreast of evolving guidelines to uphold quality, safety, and ethical standards in their continuous lamination practices.
Quality Control in Continuous Lamination
Integrating Advanced QC Systems
Embracing the digital age, continuous lamination has witnessed a paradigm shift with the integration of cutting-edge Quality Control systems. From real-time monitoring of production parameters to predictive analytics, technology stands as the sentinel, guarding against deviations and guaranteeing a consistent output that meets and exceeds industry standards.
Non-Destructive Testing Techniques
Quality control extends beyond the visible surface, delving into the core of laminated materials. Non-destructive testing techniques play a pivotal role, allowing manufacturers to scrutinize the internal structure without compromising the integrity of the final product. This proactive approach ensures that potential issues are identified and rectified before they manifest, fostering a culture of excellence.
Quality Control and Operational Efficiency
In the world of continuous lamination, quality control isn’t a standalone process; it’s an integral part of the operational ecosystem. By seamlessly integrating quality control measures into the production workflow, manufacturers not only elevate the standard of their products but also enhance overall operational efficiency. This symbiotic relationship ensures that every roll of laminated material is a testament to precision and reliability.
Skilled Inspection and Continuous Improvement
Amidst the realm of automated processes, the human touch remains irreplaceable. Skilled inspectors, armed with a keen eye for detail, play a pivotal role in quality control. Their expertise goes beyond algorithms, identifying nuances that machines might overlook. Moreover, quality control isn’t static; it’s a journey of continuous improvement, where feedback from the human element becomes the catalyst for refining and enhancing the lamination process.
Pioneering Precision in Real Time
Enter the era of smart sensors – the vanguard of real-time precision in continuous lamination. These sensors, embedded throughout the production line, gather a trove of data, enabling manufacturers to monitor and adjust parameters on the fly. This proactive approach not only minimizes the margin for error but also sets the stage for predictive maintenance, preventing potential issues before they impact production.
Quality Control Imperative
As environmental consciousness takes center stage, quality control in continuous lamination extends beyond performance metrics. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating eco-friendly materials into the lamination process, necessitating a shift in quality control paradigms. Rigorous testing now includes assessing the sustainability and environmental impact of laminated materials, ensuring that quality is synonymous with responsibility.
Redefining Inspection Processes
Step into the realm of augmented reality (AR), where the inspection process transcends conventional boundaries. AR-enhanced quality control allows inspectors to overlay digital information onto the physical world, facilitating a more immersive and comprehensive analysis. This not only expedites the inspection process but also enhances the accuracy of identifying potential defects, setting new benchmarks for quality assurance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability of Continuous Lamination
Environmental Impact:
Energy Consumption:
Continuous lamination often involves heat and pressure, contributing to energy consumption. The source of this energy can have environmental implications, depending on whether it comes from renewable or non-renewable sources.
Raw Material Usage:
The materials used in lamination, such as resins, adhesives, and substrates, may have environmental impacts depending on their source and production processes.
Waste Generation:
Lamination processes can generate waste materials, including trimmings and scraps. The disposal of these materials, especially if they are not recyclable or are difficult to manage, can contribute to environmental issues.
Chemical Emissions:
Some lamination processes may involve the use of chemicals, solvents, or adhesives that can emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air, contributing to air pollution.
Sustainability Considerations:
Material Selection:
Opting for eco-friendly and sustainable materials in the lamination process can significantly reduce the environmental impact. This includes using recycled content, bio-based materials, or those with a lower carbon footprint.
Energy Efficiency:
Implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as using renewable energy sources or optimizing heating and cooling processes, can enhance the sustainability of continuous lamination.
Waste Reduction and Recycling:
Developing strategies to minimize waste generation and promoting the recycling of materials can contribute to sustainability. This may involve reusing scrap materials or finding innovative ways to repurpose waste.
Emission Control:
Investing in technologies that capture and control emissions, especially VOCs, can mitigate the environmental impact of continuous lamination processes.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA):
Conducting a comprehensive life cycle assessment of the entire lamination process can provide insights into environmental hotspots. This assessment helps identify areas for improvement and informs decision-making for a more sustainable approach.
Regulatory Compliance:
Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and standards is essential for sustainable practices. Adhering to local and international standards helps minimize negative environmental impacts.
https://www.compositesone.com/process/continuous-lamination/
FAQs
Is continuous lamination suitable for small-scale manufacturing?
Continuous lamination can be adapted for small-scale manufacturing, offering scalability and efficiency.
What materials are commonly used in continuous lamination?
Fiberglass, carbon fiber, and various resin systems are frequently used in continuous lamination.
How does continuous lamination contribute to environmental sustainability?
Continuous lamination is evolving to incorporate eco-friendly practices and recycling initiatives, minimizing its environmental impact.
Are there any safety concerns associated with continuous lamination?
Strict adherence to safety guidelines and compliance with industry standards mitigate safety concerns in continuous lamination.
What role does automation play in continuous lamination?
Automation enhances precision, efficiency, and adaptability in continuous lamination, driving innovation in the process.
