Cellulose Fiber’s Sustainable Evolution
Cellulose fiber
Introduction
cellulose fiber is a remarkable natural resource that plays a crucial role in various industries, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic materials. Its versatility and eco-friendly attributes position it as a valuable component in the ongoing efforts towards more sustainable and responsible production practices
What is Cellulose Fiber?
Cellulose Fiber is a natural component found in the cell walls of plants, providing them with strength and rigidity. This remarkable substance is derived from renewable sources, making it an eco-conscious choice for a range of products.Transforming the fashion landscape, cellulose fiber has become the go-to material for eco-conscious designers. From breathable dresses to durable accessories, it offers a sustainable alternative without compromising style.Cellulose Fiber finds its way into our homes through products like bedding, towels, and even furniture. Embracing cellulose-based items ensures a healthier environment while contributing to the global sustainability movement.The tech industry is increasingly turning to cellulose fiber for its sustainable qualities. From biodegradable packaging to innovative electronic components, this versatile material is reshaping the technological landscape.
Manufacturing Process
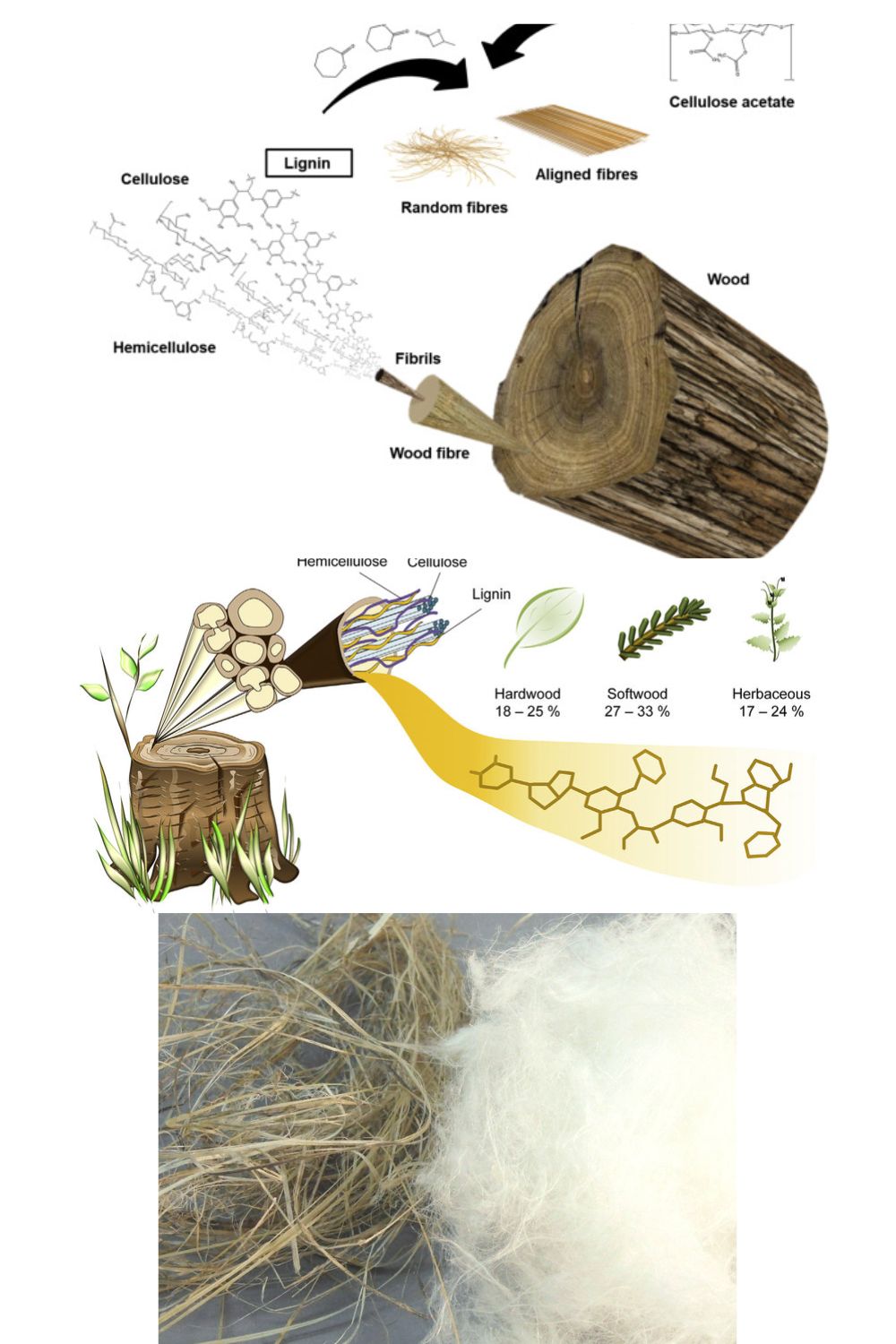
1.Cellulose Extraction
The journey commences with the extraction of cellulose, often referred to as “green gold.” Typically sourced from wood pulp or cotton, this eco-conscious material sets the stage for a sustainable textile revolution. Harvesting methods vary, but the essence lies in obtaining pure cellulose, the building block of our future textile endeavors.
2.Breaking Down Cellulose Chains
Pulping, the magical transformation of raw cellulose into a workable form, involves breaking down the cellulose chains. Whether through the Kraft or Lyocell process, the goal remains consistent – achieving a pulp that serves as the foundation for the subsequent stages. This transformative phase echoes the eco-conscious ethos, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency.
3. Spinning Wonders
With the pulped cellulose in hand, the manufacturing process takes a poetic turn – spinning wonders into existence. Through methods like the viscose, acetate, or modal processes, the cellulose undergoes a mesmerizing transformation, emerging as fine threads ready to weave tales of sustainability and resilience.
4.Creating the Fabric
The spun cellulose threads, now akin to strands of dreams, find their way to the loom. Weaving them into fabric involves a meticulous dance of precision and creativity. The result? A textile that not only embraces the touch of nature but also boasts a myriad of applications across industries.
5.Sustainable Coloring
In the realm of cellulose fiber, sustainability extends beyond its origin. The dyeing process, a crucial step in textile manufacturing, aligns with eco-conscious practices. Embracing natural dyes derived from plants and minerals, this phase ensures that every thread embodies not just color, but a commitment to a greener tomorrow.
Applications of Cellulose Fiber
Textiles and Apparel.
Cellulose fiber is commonly used in the textile industry to produce fabrics such as cotton, linen, and rayon.
Cotton, a natural cellulose fiber, is widely used in the production of comfortable and breathable clothing.
Paper and Packaging.
Cellulose fibers are a key component in paper and cardboard manufacturing.
They contribute to the strength, absorbency, and printability of paper products.
Food Industry.
Cellulose fiber is used as a dietary fiber supplement in various food products.
It can be added to enhance the texture and nutritional value of foods.
Pharmaceuticals.
Cellulose is used as an excipient in pharmaceutical formulations, acting as a binder and disintegrant in tablet production.
It is also utilized in the production of capsules and as a thickening agent in liquid medications.
Construction Materials.
Cellulose fiber can be used in the production of construction materials such as fiberboard and insulation.
It enhances the strength and insulation properties of these materials.
Automotive Industry.
Cellulose fibers are employed in the manufacturing of automotive components like reinforced plastics and composites.
These materials offer a balance of strength and lightness, contributing to fuel efficiency.
Environmental Applications.
Cellulose fibers are utilized in soil erosion control blankets and mats.
They help stabilize soil and promote vegetation growth in landscaping and environmental restoration projects.
Biodegradable Plastics.
Cellulose can be used in the production of biodegradable plastics, contributing to the reduction of environmental impact.
Cellulose fibers are often blended with other materials to reinforce textiles, improving their durability and performance.
Cellulose-based materials are used in oil and gas exploration for drilling fluids and muds.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellulose_fiber
Advantages of Cellulose Fiber
Sustainable Beauty.
In a world increasingly focused on environmental concerns, cellulose fiber emerges as a beacon of sustainability. Derived from plant-based sources, this eco-friendly material serves as a renewable resource, making it a crucial player in reducing our carbon footprint. The manufacturing process of cellulose fiber is notably energy-efficient, further contributing to its eco-conscious appeal.
Lightweight Marvel.
The lightweight nature of cellulose fiber opens doors to a plethora of applications across various industries. From the fashion realm, where it’s utilized in breathable and comfortable fabrics, to the automotive sector, benefitting from its contribution to lightweight yet sturdy components, cellulose fiber proves its versatility. Its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio makes it an ideal choice for innovative solutions in manufacturing.
Healthier Living.
Cellulose fiber takes center stage in the realm of comfort and breathability. As a natural moisture-wicking material, it ensures that products made from it remain cool and comfortable. This attribute makes cellulose fiber a popular choice in the production of bedding, clothing, and other items that come in direct contact with the skin, promoting a healthier and more comfortable lifestyle.
Eco-Chic Fashion
Fashion enthusiasts and environmentally conscious consumers alike are embracing cellulose fiber for its contribution to sustainable style. As a key component in the production of eco-friendly fabrics like Tencel and Modal, cellulose fiber allows fashionistas to make a style statement while minimizing their environmental impact. The fashion industry’s shift towards sustainability has been significantly propelled by the rise of cellulose fiber as a preferred material.
Harnessing the Future
Beyond its traditional applications, cellulose fiber is making waves in technological advancements. Researchers are exploring its potential in fields like biotechnology and electronics, showcasing its adaptability to cutting-edge innovations. As a biocompatible material, cellulose fiber holds promise in revolutionizing industries beyond our current imagination.https://anrvrar.in/thermoset-polymer-matrix-in-modern-industries/
Challenges and Solutions
Time Management Challenges:
Challenge:Inefficient use of time leading to missed deadlines.
Solution:Prioritize tasks, set realistic deadlines, and use time management techniques such as the Pomodoro Technique. Encourage the use of productivity tools to streamline workflows.
Adaptation to Change:
Challenge:Resistance to change can hinder progress.
Solution:Facilitate change management by communicating the benefits, involving team members in the decision-making process, and providing training and support during transitions.
Technological Challenges:
Challenge:Outdated technology or lack of tech literacy.
Solution:Regularly update technology, invest in training programs, and ensure that employees have access to resources that enhance their technological skills.
Diversity and Inclusion Challenges:
Challenge:Lack of diversity and inclusion can lead to a less innovative and productive environment.
Solution:Implement diversity and inclusion policies, promote a culture of respect, and provide training on unconscious bias. Encourage diverse hiring practices.
Financial Constraints:
Challenge:Limited budget for necessary resources.
Solution:Prioritize spending based on critical needs, explore cost-effective alternatives, and consider strategic partnerships or collaborations to share resources.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is cellulose fiber?
Cellulose fiber is a natural fiber derived from the cell walls of plants, primarily from wood pulp, cotton, flax, and hemp. It is a versatile and sustainable material widely used in the textile industry.
How is cellulose fiber produced?
Cellulose fiber is typically produced through a process called viscose or rayon manufacturing. This involves dissolving wood pulp in chemicals to create a viscous solution, which is then extruded into fibers and solidified.
Is cellulose fiber environmentally friendly?
Yes, cellulose fiber is considered environmentally friendly. It is derived from renewable resources, and the production process can be designed to minimize environmental impact. However, the specific environmental impact can vary depending on the production methods used.
What are the advantages of cellulose fiber?
Biodegradability: Cellulose fibers are biodegradable, making them eco-friendly.
Breathability: They have good moisture absorption and release properties, contributing to comfort in clothing.
Softness: Cellulose fibers often have a soft and comfortable feel against the skin.
Versatility: Cellulose fibers can be used in a variety of applications, including textiles, paper, and certain types of plastics.
Are there different types of cellulose fibers?
Yes, there are various types of cellulose fibers, including cotton (from cotton plants), viscose rayon (from wood pulp), lyocell (a type of rayon produced using an eco-friendly process), and hemp and flax fibers.
How does cellulose fiber compare to synthetic fibers?
Cellulose fibers have advantages over some synthetic fibers, such as being biodegradable and derived from renewable resources. They also tend to have better breathability. However, they may have limitations in terms of durability and resistance to certain environmental conditions.
